Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Li, L.*; 宮本 吾郎*; Zhang, Y.*; Li, M.*; 諸岡 聡; 及川 勝成*; 友田 陽*; 古原 忠*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 184, p.221 - 234, 2024/06
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dynamic transformation (DT) of austenite ( ) to ferrite (
) to ferrite ( ) in the hot deformation of various carbon steels was widely investigated. However, the nature of DT remains unclear due to the lack of quantitative analysis of stress partitioning between two phases and the uncertainty of local distribution of substitutional elements at the interface in multi-component carbon steels used in the previous studies. Therefore, in the present study, a binary Fe-Ni alloy with
) in the hot deformation of various carbon steels was widely investigated. However, the nature of DT remains unclear due to the lack of quantitative analysis of stress partitioning between two phases and the uncertainty of local distribution of substitutional elements at the interface in multi-component carbon steels used in the previous studies. Therefore, in the present study, a binary Fe-Ni alloy with  +
+ duplex microstructure in equilibrium was prepared and isothermally compressed in
duplex microstructure in equilibrium was prepared and isothermally compressed in  +
+ two-phase region to achieve quantitative analysis of microstructure evolution, stress partitioning and thermodynamics during DT.
two-phase region to achieve quantitative analysis of microstructure evolution, stress partitioning and thermodynamics during DT.  to
to  DT during isothermal compression and
DT during isothermal compression and  to
to  reverse transformation on isothermal annealing under unloaded condition after deformation were accompanied by Ni partitioning. The lattice strains during thermomechanical processing were obtained via in-situ neutron diffraction measurement, based on which the stress partitioning behavior between
reverse transformation on isothermal annealing under unloaded condition after deformation were accompanied by Ni partitioning. The lattice strains during thermomechanical processing were obtained via in-situ neutron diffraction measurement, based on which the stress partitioning behavior between  and
and  was discussed by using the generalized Hooke's law. A thermodynamic framework for the isothermal deformation in solids was established based on the basic laws of thermodynamics, and it was shown that the total Helmholtz free energy change in the deformable material during the isothermal process should be smaller than the work done to the deformable material. Under the present thermodynamic framework, the microstructure evolution in the isothermal compression of Fe-14Ni alloy was well explained by considering the changes in chemical free energy, plastic and elastic energies and the work done to the material. In addition, the stabilization of the soft
was discussed by using the generalized Hooke's law. A thermodynamic framework for the isothermal deformation in solids was established based on the basic laws of thermodynamics, and it was shown that the total Helmholtz free energy change in the deformable material during the isothermal process should be smaller than the work done to the deformable material. Under the present thermodynamic framework, the microstructure evolution in the isothermal compression of Fe-14Ni alloy was well explained by considering the changes in chemical free energy, plastic and elastic energies and the work done to the material. In addition, the stabilization of the soft  phase in Fe-14Ni alloy by deformation was rationalized since the
phase in Fe-14Ni alloy by deformation was rationalized since the  to
to  transformation decreased the total Helmholtz free energy by decreasing the elastic and dislocation energies.
transformation decreased the total Helmholtz free energy by decreasing the elastic and dislocation energies.
 structure transition under high pressure
structure transition under high pressure山中 高光*; 中本 有紀*; 坂田 雅文*; 清水 克哉*; 服部 高典
Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 51(1), p.4_1 - 4_10, 2024/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.34(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)FeTiO イルメナイトの中性子及び放射光X線回折と電気伝導度測定を高圧下で行った。イルメナイトの構造は28GPaまで保持された。構造解析の結果、8GPa以下ではFeO
イルメナイトの中性子及び放射光X線回折と電気伝導度測定を高圧下で行った。イルメナイトの構造は28GPaまで保持された。構造解析の結果、8GPa以下ではFeO は圧縮され、TiO
は圧縮され、TiO はほとんど圧縮されないことが分かった。抵抗率は、金属イオン対の中で原子間距離が最も短いFe-Ti方向で最も小さかった。c軸に垂直な方向の抵抗率は圧力とともに単調減少するが、c軸に沿った抵抗率は圧力とともに山なりとなった。最大エントロピー解析の結果、Fe
はほとんど圧縮されないことが分かった。抵抗率は、金属イオン対の中で原子間距離が最も短いFe-Ti方向で最も小さかった。c軸に垂直な方向の抵抗率は圧力とともに単調減少するが、c軸に沿った抵抗率は圧力とともに山なりとなった。最大エントロピー解析の結果、Fe (3
(3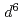 )の電子配置はTi
)の電子配置はTi (3
(3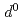 )よりも圧縮下で大きく変化することがわかった。異方的な電気伝導度とFe-Ti原子間距離の非一様な圧縮は、Feイオンの高スピン状態から中間スピン状態へのスピン転移によって説明できるかもしれない。
)よりも圧縮下で大きく変化することがわかった。異方的な電気伝導度とFe-Ti原子間距離の非一様な圧縮は、Feイオンの高スピン状態から中間スピン状態へのスピン転移によって説明できるかもしれない。
小山 元道*; 山下 享介*; 諸岡 聡; 澤口 孝宏*; Yang, Z.*; 北條 智彦*; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.
鉄と鋼, 110(3), p.197 - 204, 2024/02
The local plasticity and associated microstructure evolution in Fe-5Mn-0.1C medium-Mn steel (wt.%) were investigated in this study. Specifically, the micro-deformation mechanism during L ders banding was characterized based on multi-scale electron backscatter diffraction measurements and electron channeling contrast imaging. Similar to other medium-Mn steels, the Fe-5Mn-0.1C steel showed discontinuous macroscopic deformation, preferential plastic deformation in austenite, and deformation-induced martensitic transformation during L
ders banding was characterized based on multi-scale electron backscatter diffraction measurements and electron channeling contrast imaging. Similar to other medium-Mn steels, the Fe-5Mn-0.1C steel showed discontinuous macroscopic deformation, preferential plastic deformation in austenite, and deformation-induced martensitic transformation during L ders deformation. Hexagonal close-packed martensite was also observed as an intermediate phase. Furthermore, an in-situ neutron diffraction experiment revealed that the pre-existing body- centered cubic phase, which was mainly ferrite, was a minor deformation path, although ferrite was the major constituent phase.
ders deformation. Hexagonal close-packed martensite was also observed as an intermediate phase. Furthermore, an in-situ neutron diffraction experiment revealed that the pre-existing body- centered cubic phase, which was mainly ferrite, was a minor deformation path, although ferrite was the major constituent phase.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionZhou, Y.*; Song, W.*; Zhang, F.*; Wu, Y.*; Lei, Z.*; Jiao, M.*; Zhang, X.*; Dong, J.*; Zhang, Y.*; Yang, M.*; et al.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 971, p.172635_1 - 172635_7, 2024/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Chemistry, Physical)The grain orientation-dependent lattice strain evolution of a (TiZrHfNb)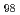
 refractory high-entropy alloy (HEA) during tensile loading has been investigated using
refractory high-entropy alloy (HEA) during tensile loading has been investigated using  neutron diffraction. The equivalent strain-hardening rate of each of the primary
neutron diffraction. The equivalent strain-hardening rate of each of the primary 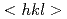 -oriented grain families was found to be relatively low, manifesting the macroscopically weak work-hardening ability of such a body-centered cubic (BCC)-structured HEA. This finding is indicative of a dislocation planar slip mode that is confined in a few single-slip planes and leads to in-plane softening by high pile-up stresses.
-oriented grain families was found to be relatively low, manifesting the macroscopically weak work-hardening ability of such a body-centered cubic (BCC)-structured HEA. This finding is indicative of a dislocation planar slip mode that is confined in a few single-slip planes and leads to in-plane softening by high pile-up stresses.
Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(4), p.32_1 - 32_13, 2023/12
Tensile deformation in situ neutron diffraction of an extruded AZ31 alloy was performed to validate conventional procedures and to develop new procedures for stress evaluation from lattice strains by diffraction measurements of HCP-structured magnesium alloys. Increases in the lattice strains with respect to the applied true stress after yielding largely vary among [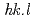 ] grains. The newly proposed procedure of stress evaluation from the lattice strains shows very high accuracy and reliability by weighting the volume fraction of [
] grains. The newly proposed procedure of stress evaluation from the lattice strains shows very high accuracy and reliability by weighting the volume fraction of [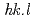 ] grains and evaluating them in many [
] grains and evaluating them in many [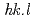 ] orientations in addition to multiplication by the diffraction elastic constant. When multiple
] orientations in addition to multiplication by the diffraction elastic constant. When multiple 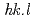 peaks cannot be obtained simultaneously, we recommend to use the 12.1 peak for stress evaluation.
peaks cannot be obtained simultaneously, we recommend to use the 12.1 peak for stress evaluation.
 B-enriched MgB
B-enriched MgB wire using a pulsed neutron source
wire using a pulsed neutron source町屋 修太郎*; 長村 光造*; 菱沼 良光*; 谷口 博康*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(4), p.34_1 - 34_17, 2023/10
Measuring the actual strain on the MgB filaments are of paramount importance, since tensile stress and strain diminish the critical current. In this study, the strain measurement using neutron diffraction during tensile loading was established. We fabricated a MgB
filaments are of paramount importance, since tensile stress and strain diminish the critical current. In this study, the strain measurement using neutron diffraction during tensile loading was established. We fabricated a MgB wire enriched with boron-11, an isotope having a smaller neutron absorption cross- section than natural boron, and succeeded in obtaining changes in the lattice constant under tensile loading through Rietveld analysis.
wire enriched with boron-11, an isotope having a smaller neutron absorption cross- section than natural boron, and succeeded in obtaining changes in the lattice constant under tensile loading through Rietveld analysis.
Harjo, S.
日本結晶学会誌, 65(3), p.178 - 182, 2023/08
Observations of deformation behavior of high entropy alloys using  neutron diffraction measurements during deformation at various temperatures are reviewed. Neutrons are used to investigate stresses and crystallographic microstructures inside engineering materials, taking advantage of their large penetrating power and the ability to see the arrangement of atoms by diffraction methods. The important structural details of high entropy alloys such as internal stresses, phase conditions, dislocations, texture etc. are discussed in relation to the deformation conditions. Some highlights are introduced: (a) Cooperative deformation in CrMnFeCoNi alloy at ultralow temperatures, (b) Stacking fault energies in CrFeCoNi and CrCoNi alloys, and (c) Load redistribution in eutectic high entropy alloy AlCoCrFeNi
neutron diffraction measurements during deformation at various temperatures are reviewed. Neutrons are used to investigate stresses and crystallographic microstructures inside engineering materials, taking advantage of their large penetrating power and the ability to see the arrangement of atoms by diffraction methods. The important structural details of high entropy alloys such as internal stresses, phase conditions, dislocations, texture etc. are discussed in relation to the deformation conditions. Some highlights are introduced: (a) Cooperative deformation in CrMnFeCoNi alloy at ultralow temperatures, (b) Stacking fault energies in CrFeCoNi and CrCoNi alloys, and (c) Load redistribution in eutectic high entropy alloy AlCoCrFeNi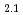 during high temperature deformation.
during high temperature deformation.
高木 寛貴*; 高木 里奈*; 見波 将*; 野本 拓也*; 大石 一城*; 鈴木 通人*; 柳 有起*; 平山 元昭*; Khanh, N.*; 軽部 皓介*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(7), p.961 - 968, 2023/07
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:96.03(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In ferromagnets, electric current generally induces a transverse Hall voltage in proportion to the internal magnetization. This effect is frequently used for electrical readout of the spin up and down states. While these properties are usually not expected in antiferromagnets, recent theoretical studies predicted that non-coplanar antiferromagnetic order with finite scalar spin chirality - meaning a solid angle spanned by neighboring spins - can induce a large spontaneous Hall effect even without net magnetization or external magnetic field. This phenomenon, the spontaneous topological Hall effect, can potentially be used for the efficient electrical readout of the antiferromagnetic states, but it has not been experimentally verified due to a lack of appropriate materials hosting such magnetism. Here, we report the discovery of all-in-all-out type non-coplanar antiferromagnetic order in triangular lattice compounds CoTa S
S and CoNb
and CoNb S
S . These compounds are reported to host unconventionally large spontaneous Hall effect despite their vanishingly small net magnetization, and our analysis reveals that it can be explained in terms of the topological Hall effect that originates from the fictitious magnetic field associated with scalar spin chirality. These results indicate that the scalar spin chirality mechanism offers a promising route to the realisation of giant spontaneous Hall response even in compensated antiferromagnets, and highlight intercalated van der Waals magnets as a promising quasi-two-dimensional material platform to enable various nontrivial ways of electrical reading and possible writing of non-coplanar antiferromagnetic domains.
. These compounds are reported to host unconventionally large spontaneous Hall effect despite their vanishingly small net magnetization, and our analysis reveals that it can be explained in terms of the topological Hall effect that originates from the fictitious magnetic field associated with scalar spin chirality. These results indicate that the scalar spin chirality mechanism offers a promising route to the realisation of giant spontaneous Hall response even in compensated antiferromagnets, and highlight intercalated van der Waals magnets as a promising quasi-two-dimensional material platform to enable various nontrivial ways of electrical reading and possible writing of non-coplanar antiferromagnetic domains.
安江 歩夢*; 川上 真由*; 小林 謙祐*; Kim, J.; 宮津 裕次*; 西尾 悠平*; 向井 智久*; 諸岡 聡; 兼松 学*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(2), p.15_1 - 15_14, 2023/05
Neutron diffraction is a noncontact method that can measure the rebar strain inside concrete. In this method, rebar strain and stress are calculated using the diffraction profile of neutrons irradiated during a specific time period. In general, measurement accuracy improves with the length of the measurement time. However, in previous studies, the measurement time was determined empirically, which makes the accuracy and reliability of the measurement results unclear. In this study, the relationship between the measurement time and the measurement standard deviation was examined for reinforced concrete specimens under different conditions. The aim was to clarify the accuracy of the measurement of rebar stress using the neutron diffraction method. It was found that if the optical setup of the neutron diffractometer and the conditions of the specimen are the same, there is a unique relationship between the diffraction intensity and the rebar stress standard deviation. Furthermore, using this unique relationship, this paper proposes a method for determining the measurement time from the allowable accuracy of the rebar stress, which ensures the accuracy of the neutron diffraction method.
Kwon, H.*; Sathiyamoorthi, P.*; Gangaraju, M. K.*; Zargaran, A.*; Wang, J.*; Heo, Y.-U.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Lee, B.-J.*; Kim, H. S.*
Acta Materialia, 248, p.118810_1 - 118810_12, 2023/04
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:99.28(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Maraging steels, known for ultrahigh strength and good fracture toughness, derive their superior properties from lath martensite structure with high-density nanoprecipitates. In this work, we designed a novel Fe-based medium-entropy alloy with a chemical composition of Fe Co
Co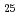 Ni
Ni Mo
Mo in atomic% by utilizing the characteristics of the maraging steels. By a single-step aging of only 10 min at 650
in atomic% by utilizing the characteristics of the maraging steels. By a single-step aging of only 10 min at 650  C, the alloy showed microstructures consisting of a very high number density of (Fe, Co, Ni)
C, the alloy showed microstructures consisting of a very high number density of (Fe, Co, Ni) Mo
Mo -type nanoprecipitates in lath martensite structure and reverted FCC phase, which led to ultrahigh yield strength higher than 2 GPa. This work demonstrates a novel direction to produce strong and ductile materials by expanding the horizons of material design with the aid of high-entropy concept and overcoming the limits of conventional materials.
-type nanoprecipitates in lath martensite structure and reverted FCC phase, which led to ultrahigh yield strength higher than 2 GPa. This work demonstrates a novel direction to produce strong and ductile materials by expanding the horizons of material design with the aid of high-entropy concept and overcoming the limits of conventional materials.
Wang, Y.*; 友田 陽*; 大村 孝仁*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.
Materialia, 27, p.101685_1 - 101685_9, 2023/03
The evolution of internal stress during displacive transformation is a topic of continuous debate. Neutron diffraction was used to study the isothermal bainite transformation in a 0.4 C low alloyed steel from 773 to 623 K to provide a clearer basis for discussion regarding the change in the austenite lattice parameter. According to diffraction profile analysis, fresh bainite possesses a body-centered tetragonal structure, and its c/a ratio decreases rapidly over time. The austenite lattice parameter increases or decreases depending on whether the transformation temperature is above or below the nose of the Time-Temperature-Transformation (TTT) curve. This isothermal transformation behavior can be divided into two categories: above and below the nose of TTT curve, which correspond to the upper and lower bainites, respectively. The internal stresses caused by the transformation strains are relaxed by dislocation motion and vacancy formation. The yielded dislocations and vacancies not only affect the broadening of both austenite and bainitic ferrite diffraction peaks but also the lattice parameter.
 Mg/LPSO dual-phase magnesium alloy monitored by
Mg/LPSO dual-phase magnesium alloy monitored by  neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionHarjo, S.; Gong, W.; 相澤 一也; 川崎 卓郎; 山崎 倫昭*; 眞山 剛*; 河村 能人*
Materials Transactions, 64(4), p.766 - 773, 2023/02
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:90.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To elucidate the effect of extrusion ratio in hot-extrusion on the deformation behavior during compression of Mg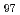 Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy containing about 25-vol% long-period stacking ordered phase (LPSO) in the HCP structured
alloy containing about 25-vol% long-period stacking ordered phase (LPSO) in the HCP structured  matrix (
matrix ( Mg),
Mg),  neutron diffraction measurements were performed under compressive loading using four types of samples: as-cast and after hot extrusion at 623 K with extrusion ratios of 5.0, 7.5 and 12.5. The macroscopic yielding was observed to appear by the occurrence of basal slip of
neutron diffraction measurements were performed under compressive loading using four types of samples: as-cast and after hot extrusion at 623 K with extrusion ratios of 5.0, 7.5 and 12.5. The macroscopic yielding was observed to appear by the occurrence of basal slip of  Mg in the as-cast sample and at the onset of twinning in the hot extruded samples. The applied stress to initiate slip, twinning, and kinking increased by hot extrusion and then decreased with increasing extrusion ratio. LPSO shared higher stress than
Mg in the as-cast sample and at the onset of twinning in the hot extruded samples. The applied stress to initiate slip, twinning, and kinking increased by hot extrusion and then decreased with increasing extrusion ratio. LPSO shared higher stress than  Mg and the ratio to the strength increased as the extrusion ratio increased.
Mg and the ratio to the strength increased as the extrusion ratio increased.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffraction澤口 孝宏*; 友田 陽*; 吉中 奎貴*; Harjo, S.
Acta Materialia, 242, p.118494_1 - 118494_14, 2023/01
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:45.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Fe-Mn-Si-based alloys, show superior resistance to plastic fatigue compared to the conventional steels, which is ascribed to the reversible back-and-forth movement of Shockley partial dislocations associated with a reversible martensitic transformation between the face-centered cubic  -austenite and hexagonal close-packed
-austenite and hexagonal close-packed  -martensite. The purpose of this study was to gather evidence of the reversible martensitic transformation using in situ neutron diffraction under cyclic loading. Three Fe-30Mn-Si-Al alloys with different Gibbs free energy differences at 298 K were studied to unravel the effect of phase stability on the degree of reversibility.
-martensite. The purpose of this study was to gather evidence of the reversible martensitic transformation using in situ neutron diffraction under cyclic loading. Three Fe-30Mn-Si-Al alloys with different Gibbs free energy differences at 298 K were studied to unravel the effect of phase stability on the degree of reversibility.
 phase to
phase to  phase in zirconium alloy revealed by in-situ neutron diffraction during high temperature deformation
phase in zirconium alloy revealed by in-situ neutron diffraction during high temperature deformationGuo, B.*; Mao, W.; Chong, Y.*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Chen, H.*; Jonas, J. J.*; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 242, p.118427_1 - 118427_11, 2023/01
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:64.46(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dynamic transformation from alpha (HCP) to beta (BCC) phase in a zirconium alloy was revealed by the use of in-situ neutron diffraction during hot compression. The dynamic transformation was unexpectedly detected during isothermal compression at temperatures of 900 C and 950
C and 950 C (alpha + beta two-phase region) and strain rates of 0.01 s
C (alpha + beta two-phase region) and strain rates of 0.01 s and 0.001 s
and 0.001 s , even though equilibrium two-phase states were achieved prior to the hot compression. Dynamic transformation was accompanied by diffusion of Sn from beta to alpha phase, which resulted in changes of lattice parameters and a characteristic microstructure of alpha grains. The details of dynamic transformation are discussed using the evolution of lattice constants.
, even though equilibrium two-phase states were achieved prior to the hot compression. Dynamic transformation was accompanied by diffusion of Sn from beta to alpha phase, which resulted in changes of lattice parameters and a characteristic microstructure of alpha grains. The details of dynamic transformation are discussed using the evolution of lattice constants.
川崎 卓郎; 高橋 美和子*; 鬼柳 亮嗣; 大原 高志
Acta Crystallographica Section C; Structural Chemistry (Internet), 78(12), p.743 - 748, 2022/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Structural changes of the raffinose crystal on dehydration from the pentahydrate to the tetrahydrate were investigated by single-crystal time-of-flight neutron diffraction. It was revealed that during the dehydration, rearrangement occurs in the hydrogen bonds related to the lost water molecule, while the symmetry of the crystal structure is retained. The hydrogen-bonding status of raffinose pentahydrate and tetrahydrate were discussed comprehensively according to Jeffrey's hydrogen-bonding classification. It was shown that water molecules are hydrogen bonded to the surrounding molecules by 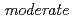 O-H...O hydrogen bonds and
O-H...O hydrogen bonds and 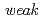 C-H...O hydrogen bonds, and the number of these two types of hydrogen bonds determines the water molecules that are removed by dehydration. The lattice constant c showed a significant decrease on dehydration and further dehydration leads to loss of crystallinity of the raffinose crystals.
C-H...O hydrogen bonds, and the number of these two types of hydrogen bonds determines the water molecules that are removed by dehydration. The lattice constant c showed a significant decrease on dehydration and further dehydration leads to loss of crystallinity of the raffinose crystals.
 ders deformation in an Fe-5Mn-0.1C medium-Mn steel
ders deformation in an Fe-5Mn-0.1C medium-Mn steel小山 元道*; 山下 享介*; 諸岡 聡; 澤口 孝宏*; Yang, Z.*; 北條 智彦*; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.
ISIJ International, 62(10), p.2036 - 2042, 2022/10
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:64.46(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)The local plasticity and associated microstructure evolution in Fe-5Mn-0.1C medium-Mn steel (wt.%) were investigated in this study. Specifically, the micro-deformation mechanism during L ders banding was characterized based on multi-scale electron backscatter diffraction measurements and electron channeling contrast imaging. Similar to other medium-Mn steels, the Fe-5Mn-0.1C steel showed discontinuous macroscopic deformation, preferential plastic deformation in austenite, and deformation-induced martensitic transformation during L
ders banding was characterized based on multi-scale electron backscatter diffraction measurements and electron channeling contrast imaging. Similar to other medium-Mn steels, the Fe-5Mn-0.1C steel showed discontinuous macroscopic deformation, preferential plastic deformation in austenite, and deformation-induced martensitic transformation during L ders deformation. Hexagonal close-packed martensite was also observed as an intermediate phase. Furthermore, an in-situ neutron diffraction experiment revealed that the pre-existing body-centered cubic phase, which was mainly ferrite, was a minor deformation path, although ferrite was the major constituent phase.
ders deformation. Hexagonal close-packed martensite was also observed as an intermediate phase. Furthermore, an in-situ neutron diffraction experiment revealed that the pre-existing body-centered cubic phase, which was mainly ferrite, was a minor deformation path, although ferrite was the major constituent phase.
熊谷 正芳*; 黒田 雅利*; 松野 崇*; Harjo, S.; 秋田 貢一*
Materials & Design, 221, p.110965_1 - 110965_8, 2022/09
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:41.53(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Microstructural evolution in austenitic stainless steels during cyclic plastic deformation has been studied via diffraction line profile analysis; however, their microstructure-dependent mechanical response upon stress partitioning in the matrix (austenite) and deformation-induced martensite has remained largely unexplored. In this study, the stress response analysis of austenitic stainless steel was performed using neutron diffraction, to evaluate the phase stresses in the austenite and martensite, and the relation with dislocation data was discussed.
 Co
Co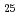 Ni
Ni Al
Al Ti
Ti Mo
Mo medium-entropy alloy; In situ neutron diffraction analysis
medium-entropy alloy; In situ neutron diffraction analysisKwon, H.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Gong, W.; Jeong, S. G.*; Kim, E. S.*; Sathiyamoorthi, P.*; 加藤 秀実*; Kim, H. S.*
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 23(1), p.579 - 586, 2022/00
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:66.14(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Metastability engineering is a strategy to enhance the strength and ductility of alloys via deliberately lowering phase stability and prompting deformation-induced martensitic transformation. In this work, the martensitic transformation and its effect on the mechanical response of a Fe Co
Co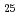 Ni
Ni Al
Al Ti
Ti Mo
Mo medium-entropy alloy (MEA) were studied by in situ neutron diffraction under tensile loading. This work shows how great a role FCC to BCC martensitic transformation can play in enhancing the mechanical properties of ferrous MEAs.
medium-entropy alloy (MEA) were studied by in situ neutron diffraction under tensile loading. This work shows how great a role FCC to BCC martensitic transformation can play in enhancing the mechanical properties of ferrous MEAs.
Liss, K.-D.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 相澤 一也; 徐 平光
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 869, p.159232_1 - 159232_9, 2021/07
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:47.82(Chemistry, Physical)The aluminium strontium master alloy Al-10Sr has been investigated by in-situ neutron diffraction upon a heating-cooling cycle, revealing composition, crystallographic structure, lattice evolution and linear thermal expansion coefficients. Expansion of the Al matrix between (23.5 ... 26.7) 10
10 K
K depends on temperature and fits well to the literature values, extrapolating to higher temperature at 800 K. Thermal expansion is highly anisotropic for tetragonal Al
depends on temperature and fits well to the literature values, extrapolating to higher temperature at 800 K. Thermal expansion is highly anisotropic for tetragonal Al Sr by a factor of 1.86 with values of 20.8 and 11.1
Sr by a factor of 1.86 with values of 20.8 and 11.1 10
10 K
K in
in  and
and  -axis. The even large discrepancy to the Al matrix is prone to residual intergranular phase stresses, explaining the brittleness of such composite material. Upon first heating, recovery of the initially plastically deformed materials is observed until 600 K and 700 K, for Al
-axis. The even large discrepancy to the Al matrix is prone to residual intergranular phase stresses, explaining the brittleness of such composite material. Upon first heating, recovery of the initially plastically deformed materials is observed until 600 K and 700 K, for Al Sr and Al. Rietveld analysis refines the 4
Sr and Al. Rietveld analysis refines the 4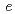 Wyckoff positions of the
Wyckoff positions of the 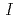 4/
4/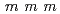 crystal structure to
crystal structure to 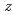 = 0.39 revealing that local tetrahedrons are regular while local hexagons are stretched, in contrast to the literature. Its lattice parameters report to
= 0.39 revealing that local tetrahedrons are regular while local hexagons are stretched, in contrast to the literature. Its lattice parameters report to 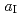 = 4.44240(48)
= 4.44240(48)  ,
, 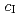 = 11.0836(15)
= 11.0836(15)  at 300 K. Furthermore, the manuscript demonstrates full technical analysis of the neutron data. Findings feed into data bases and an outlook for improving mechanical properties of Al
at 300 K. Furthermore, the manuscript demonstrates full technical analysis of the neutron data. Findings feed into data bases and an outlook for improving mechanical properties of Al Sr composites is given.
Sr composites is given.
山下 享介*; 古賀 紀光*; 川崎 卓郎; 諸岡 聡; 友野 翔平*; 梅澤 修*; Harjo, S.
Materials Science & Engineering A, 819, p.141509_1 - 141509_10, 2021/07
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:83.73(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)In-situ neutron diffraction measurements were performed on a cold-rolled copper-iron (Cu-Fe) alloy during tensile tests at 293 K and 150 K. The roles of Cu and Fe on the deformation behavior of alloys were discussed and clarified. The strength and work-hardening rate of the alloy increased with decreasing test temperature. Furthermore, the phase stress of Fe increased considerably with decreasing test temperature; however, the response of this stress to the applied true stress exhibited no dependence on the temperature. The phase stresses of Cu changed only slightly with decreasing test temperature. However, the Cu phase stress response to the applied true stress increased with decreasing test temperature, indicating an increase in the work-hardening rate. The strengthening of Fe and the increase in the work-hardening of Cu contributed to an increase in the strength and work-hardening rate of the Cu-Fe alloy at low temperatures.